本院管坤良博士和赵斌博士2011年8月1日在Nature Cell Biology杂志发表特邀综述文章“The Hippo pathway in organ size control, tissue regeneration and stem cell self-renewal.”其中赵斌博士为第一作者,管坤良博士为通讯作者。
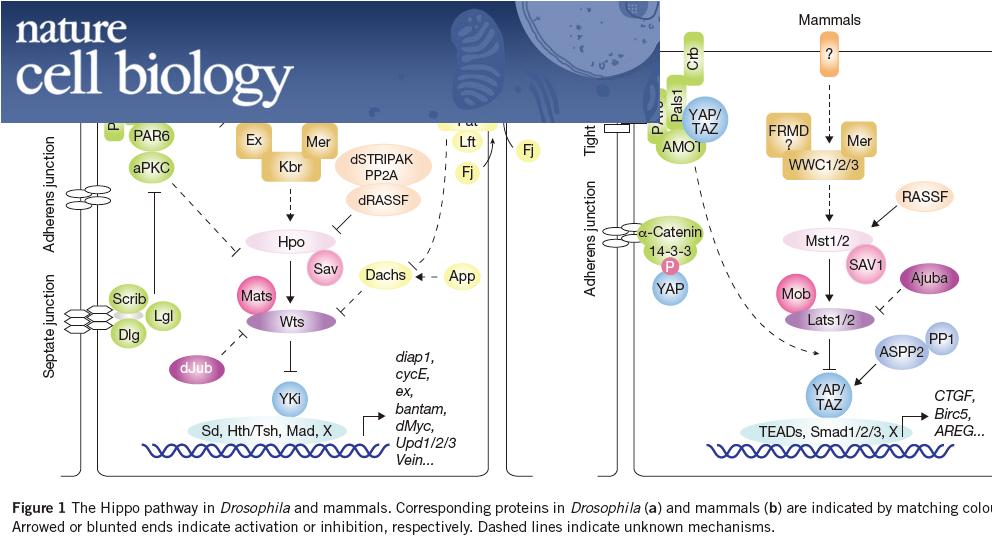
器官和机体的大小是多细胞生物最基本的特征之一。例如大象的体形总是要比小鼠大得多,又例如哺乳动物的肝脏部分切除后能精确再生到原来的大小。然而,这些有趣的生物学现象却长期未能得到分子水平的解释。最新的研究表明一条在进化上高度保守的叫做Hippo通路的新的细胞信号传导途径对器官大小的调控起着至关重要的作用。例如敲除该通路中的激酶基因Mst1/2导致小鼠肝脏过度生长至正常大小的四倍。Hippo通路的蛋白激酶能够导致YAP和TAZ转录辅激活因子的磷酸化和失活进而抑制细胞增殖,促进细胞凋亡。进一步的研究显示这条信号通路还调控干细胞自我更新及组织再生,特别是与癌症的发生密切相关。因而该通路的研究不但是发育生物学的重要课题,而且对人类疾病的治疗具有指导意义。最新的证据还表明Hippo通路受细胞极性,细胞粘附和细胞连接蛋白的调控。本文总结了当今关于Hippo通路组成和调控的理解,并讨论了Hippo通路可能如何整合细胞极性和细胞连接的信号来调控器官大小和组织再生。


Bin Zhao; Karen Tumaneng; Kun-Liang Guan
【Abstract 】
Precise control of organ size is crucial during animal development and regeneration. In Drosophila and mammals, studies over the past decade have uncovered a critical role for the Hippo tumour-suppressor pathway in the regulation of organ size. Dysregulation of this pathway leads to massive overgrowth of tissue. The Hippo signalling pathway is highly conserved and limits organ size by phosphorylating and inhibiting the transcription co-activators YAP and TAZ in mammals and Yki in Drosophila, key regulators of proliferation and apoptosis. The Hippo pathway also has a critical role in the self-renewal and expansion of stem cells and tissue-specific progenitor cells, and has important functions in tissue regeneration. Emerging evidence shows that the Hippo pathway is regulated by cell polarity, cell adhesion and cell junction proteins. In this review we summarize current understanding of the composition and regulation of the Hippo pathway, and discuss how cell polarity and cell adhesion proteins inform the role of this pathway in organ size control and regeneration.
Precise control of organ size is crucial during animal development and regeneration. In Drosophila and mammals, studies over the past decade have uncovered a critical role for the Hippo tumour-suppressor pathway in the regulation of organ size. Dysregulation of this pathway leads to massive overgrowth of tissue. The Hippo signalling pathway is highly conserved and limits organ size by phosphorylating and inhibiting the transcription co-activators YAP and TAZ in mammals and Yki in Drosophila, key regulators of proliferation and apoptosis. The Hippo pathway also has a critical role in the self-renewal and expansion of stem cells and tissue-specific progenitor cells, and has important functions in tissue regeneration. Emerging evidence shows that the Hippo pathway is regulated by cell polarity, cell adhesion and cell junction proteins. In this review we summarize current understanding of the composition and regulation of the Hippo pathway, and discuss how cell polarity and cell adhesion proteins inform the role of this pathway in organ size control and regeneration.
The Hippo pathway in organ size control, tissue regeneration and stem cell self-renewal




